Browsing Success: UH 60 Helicopter Maintenance Ideal Practices
Browsing Success: UH 60 Helicopter Maintenance Ideal Practices
Blog Article
Browsing Uh 60 Helicopter Laws and Compliance Demands

Regulatory Framework Introduction
The regulative framework governing UH-60 helicopter operations includes a complicated set of regulations and requirements established by aviation authorities. These guidelines are developed to guarantee the effective and secure operation of UH-60 helicopters in various atmospheres. The Federal Air Travel Administration (FAA) plays a central role in establishing and applying these policies, which cover a vast array of operational facets, including airworthiness requirements, pilot certifications, maintenance requirements, and operational procedures.
Compliance with these regulations is vital for helicopter operators to preserve the greatest degrees of security and operational honesty. Failing to comply with these laws can result in severe repercussions, including mishaps, injuries, and governing sanctions. Helicopter operators need to stay notified concerning the latest regulatory growths and guarantee that their operations are in full conformity with all appropriate guidelines and criteria.
Airworthiness Instructions and Inspections
Among the governing structure regulating UH-60 helicopter procedures, an important focus exists on compliance with Airworthiness Directives and conducting extensive assessments to promote safety and security criteria and operational dependability. Airworthiness Instructions (Advertisements) are released by aeronautics authorities to resolve dangerous conditions in airplane, including the UH-60 helicopter, and required certain activities to be taken by proprietors or drivers. Compliance with ADs is mandatory, and failure to follow these directives can cause severe effects, including grounding of the aircraft.
Normal assessments are extremely important to making certain the airworthiness of UH-60 helicopters. These evaluations encompass a variety of checks, from regular daily assessments performed by pilots prior to and after trips to a lot more detailed scheduled upkeep inspections accomplished by certified mechanics. Furthermore, unique examinations may be called for based on details conditions or incidents. By adhering to a rigorous inspection regimen, drivers can find and attend to possible problems immediately, therefore boosting the security and dependability of UH-60 helicopter operations.
Pilot Qualifications and Training
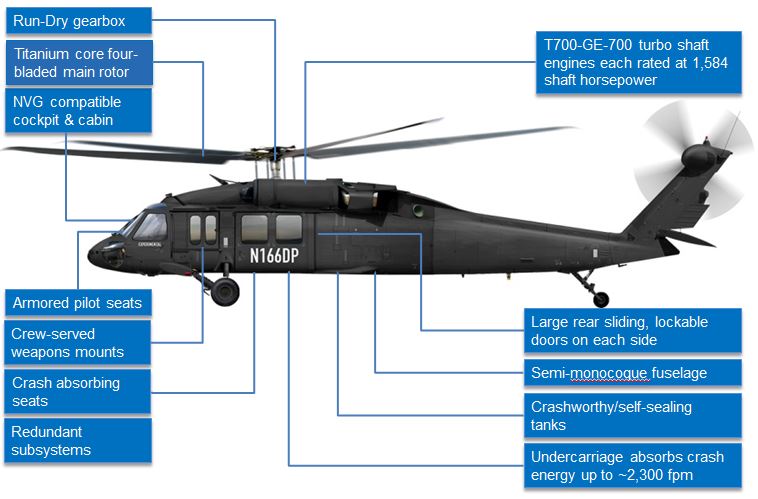
Pilot training for UH-60 helicopters is detailed and covers a wide variety of topics, consisting of airplane systems, emergency treatments, navigating, and mission-specific training. In addition, pilots undergo simulator training to practice different emergency situation circumstances in a regulated atmosphere. This training helps pilots establish the essential abilities to manage difficult situations properly.


Furthermore, ongoing training and professional development are important for UH-60 pilots to remain current with the most up to date policies, modern technology, and ideal techniques. By purchasing pilot qualifications and training, drivers can enhance security, enhance performance, and make certain compliance with regulative resource demands in the procedure of UH-60 helicopters.
Functional Limitations and Needs
Pilot credentials and training offer as the foundation for comprehending the functional restrictions and needs related to UH-60 helicopter procedures (uh 60). These functional restrictions are established to ensure the security of the crew, travelers, and the airplane itself. Operational constraints might consist of variables such as weather, weight constraints, elevation constraints, and functional boundaries. It is important for pilots to be fluent in these constraints to make informed choices throughout trip operations. Furthermore, compliance demands, such as sticking to particular trip paths, interaction protocols, and emergency situation treatments, are crucial for maintaining operational safety and security and governing compliance. Pilots need to remain present with all functional limitations and needs via regular training, instructions, and examines to minimize dangers and make sure secure and effective UH-60 helicopter operations. By prioritizing adherence to these functional guidelines, pilots can improve read more the overall safety and effectiveness of their missions while upholding regulatory standards.
Emergency Situation Procedures and Conformity Screening
Effective emergency situation procedures and complete conformity screening are important elements of preserving operational safety and security and regulatory adherence in UH-60 helicopter procedures. Emergency treatments include protocols for different situations, including engine failures, fires, hydraulic concerns, and extra. Pilots and crew members have to be fluent in these procedures to respond swiftly and properly in emergencies. Routine compliance screening makes certain that the helicopter satisfies all regulative needs stated by aviation authorities. This testing involves complete examinations, checks, and examinations to validate that the airplane is airworthy and in compliance with all relevant guidelines.
Compliance testing additionally encompasses tools onboard the UH-60, such as interaction systems, navigation tools, and safety gear. Guaranteeing that all tools is working properly and meets regulatory standards is essential for safe operations. Additionally, compliance screening might include simulations of emergency situation scenarios to evaluate the crew's reaction and the helicopter's efficiency under tension. By focusing on emergency treatments and conformity screening, UH-60 operators site link can alleviate risks and demonstrate their dedication to safety and security and regulative compliance.
Conclusion
Finally, adherence to regulatory structure, conformity with airworthiness regulations, pilot certifications and training, operational constraints, and emergency procedures are necessary for navigating the guidelines and demands of running a UH-60 helicopter. uh 60. It is vital for operators to focus on safety and guarantee complete conformity with all appropriate guidelines to preserve the airworthiness and functional honesty of the airplane
Navigating the governing landscape surrounding UH-60 helicopter procedures requires a nuanced understanding of the complex internet of policies and compliance requirements.Compliance with these regulations is vital for helicopter operators to preserve the greatest levels of safety and security and operational honesty.In the middle of the governing framework governing UH-60 helicopter operations, an essential focus exists on compliance with Airworthiness Directives and conducting complete inspections to maintain safety and security standards and functional integrity.Reliable emergency situation procedures and complete compliance testing are critical parts of preserving functional safety and governing adherence in UH-60 helicopter procedures. Routine conformity testing makes certain that the helicopter fulfills all regulative requirements set forth by aeronautics authorities.
Report this page